Are you also thinking How Does High-Temperature Incineration Work, so this blog is for you to know how Incineration process actually work at High-Temperature. Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials. High-temperature incinerators are used to reduce the volume of waste, destroy pathogens, and eliminate hazardous components — especially in medical, industrial, and municipal waste.
- Looking for High – Temperature Incinerator ?
- How Does High-Temperature Incineration Work?
- High-Temperature Medical Waste Incinerators
- What Types of Medical Waste are Incinerated ?
- Operational Costs of Medical Waste Incinerators
- Temperature of an Incinerator Burning Waste: High-Temperature Incineration Work
- Frequently Asked Questions about High-Temperature Incineration
Looking for High – Temperature Incinerator ?
Connect us at info@bionicsscientific.com
How Does High-Temperature Incineration Work?
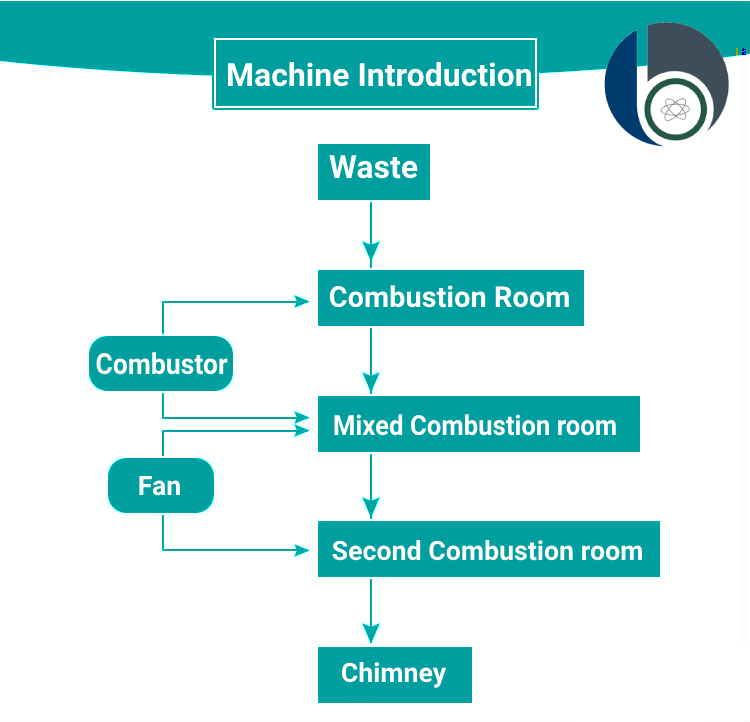
As we know incineration process can not give us the desired result without using high-temperature. It can work well, so Incineration involves step by step process designed to efficiently break down waste materials and reduce harmful emissions.
Pre-treatment: Waste is put through a process of sorting and shredding to ensure a consistent material flow and optimize the process of burning within the hospital incinerator.
Incineration chamber and high-temperature: We put Pre-treated waste into a furnace where it is burned at extremely high temperatures. This strong heat breaks down the waste into smaller molecules. Ash removal and flue gas treatment: The combustion process produces ash, a left material that requires proper disposal. Additionally, flue gases contain emissions are treated to remove pollutants before being released into the atmosphere.
High-Temperature Medical Waste Incinerators

High-temperature medical waste incinerators play a vital role in the compliant and safely dispose of various types of healthcare and clinical waste. These waste incinerator systems are used by hospitals, dental clinics, veterinary centers, care homes, universities, research labs, and other healthcare-related facilities. They securely destroy yellow-bagged clinical waste, which includes highly infectious materials, sharps, cytotoxic or cytostatic waste, pharmaceutical waste, and anatomical waste.
These incinerators are designed to safely destroy yellow-bagged clinical waste, which typically includes highly infectious materials, sharps (like needles and scalpels), cytotoxic and cytostatic waste, expired or unused pharmaceuticals, and anatomical waste such as human tissues or organs. By operating at extremely high temperatures—often exceeding 850°C to 1100°C—these systems ensure the complete combustion of organic matter, neutralizing pathogens and reducing the volume of waste by up to 90%.
Moreover, modern medical incinerators are equipped with advanced emission control systems that minimize the release of harmful pollutants, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations. This makes them an essential solution for healthcare facilities seeking a reliable and regulatory-compliant method of hazardous waste disposal.
What Types of Medical Waste are Incinerated ?
It is essential to consult your waste vendor’s Waste Acceptance Policy, which clearly defines the types of waste they accept, the conditions required for acceptance, and any restrictions that may apply. Our medical waste incinerators accept following types of waste:
- Pathological Waste: Includes human or animal tissues, organs, limbs, surgical specimens, and other body parts. These must be free of chemical preservatives
- Paraffin Wax Blocks: Tissue-embedded blocks from humans or animals, required to be packaged according to the detailed packaging guidelines available on our website
- Non-Hazardous Pharmaceutical Waste: Consists of pharmaceuticals not classified as hazardous by relevant state authority. Proper segregation and packaging are still required.
- Trace Chemotherapy Waste: Includes items contaminated by, or that have previously contained, chemotherapeutic agents. These must be handled as trace hazardous waste, following specific disposal guidelines.
Operational Costs of Medical Waste Incinerators
Running a medical waste incinerator comes with several expenses:
- Initial investment in equipment and setup
- Fuel consumption, especially for high-temperature operations
- Labor and maintenance to ensure 24/7 safe operation
- Regulatory compliance, such as emissions controls and certifications
Efficient management of these costs ensures that incineration remains one of the most reliable and sustainable methods for clinical waste disposal.
Temperature of an Incinerator Burning Waste: High-Temperature Incineration Work
The actual temperature within the incinerator can fluctuate depending on the specific waste composition and the operational stage. However, it’s crucial to maintain the minimum operating temperature for efficient and clean combustion.
- High-temperature incineration utilizes intense heat to break down waste materials.
- The process involves pre-treatment, combustion, and gas treatment to minimize harmful emissions.
- Incinerators typically operate between 850°C and 1200°C for efficient and clean combustion.
Did You Know?
Modern incineration facilities use sophisticated pollution control systems to minimize the environmental impact. These systems can capture and remove harmful pollutants like acid gases, heavy metals, and particulate matter from the flue gas.
Pros of High Temperature Incineration
- Reduces landfill waste and associated environmental concerns.
- Generates energy that can be used for electricity or heating.
- Can handle certain types of waste that are difficult to recycle.
Cons of High Temperature Incineration
- May release pollutants if not properly managed.
- Ash residue from incineration requires further disposal.
- Incineration doesn’t eliminate waste; it transforms it.
Frequently Asked Questions about High-Temperature Incineration



