Hot air ovens are essential equipment used for sterilization and drying in many industries. Their ability to maintain a constant temperature makes them great for processes where precise heat is required. This article explains what hot air ovens are, how they work, their uses, benefits and maintenance methods.
Table of Contents
What is a Hot Air Oven?
A hot oven is a type of laboratory equipment used to dry and heat materials. Unlike autoclaves, which use pressurized steam, hot air ovens use circulating air to sterilize. It is used in medical and industrial environments to ensure the cleanliness and safety of equipment and materials.
Looking for Hot Air Oven ?
We are india based Hot Air Oven manufacturers providing 22 Litres to 400 Litres Hot Air Ovens for all purposes, we can design and manufacture hot air ovens meeting customer provided temperature range, sizes and capacities. Connect at info@bionicsscientific.com
How Does a Hot Air Oven Work?
Hot air ovens heat things evenly by circulating hot air inside the chamber. Here is a simple description of the process.
- Heating Element: Heats the air inside the oven.
- Fan: Ensures uniform temperature distribution by circulating hot air.
- Thermostat: Controls the temperature to maintain a set point.
- Insulated Chamber: Ensures minimum heat loss and smooth use of energy.
The process typically involves placing items on racks within the oven, setting the desired temperature and duration, and allowing the oven to heat and sterilize the items.
Hot Air Oven Diagram
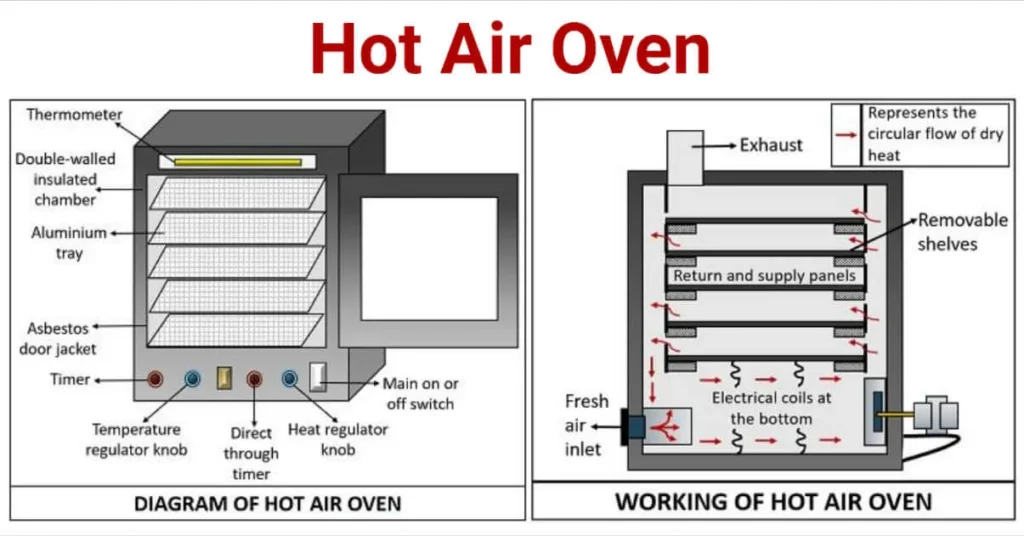
Principle of Hot Air Oven
A hot-air oven relies on dry heat sterilization, where convection, conduction, and radiation play interlocking roles. Electrical elements warm the enclosed air, and circulating fans promote an even temperature profile throughout the chamber. Solid samples absorb this energy; the outer skin heats first, and conduction gradually routes that heat inward. In microbial cells, the rapid loss of intracellular moisture accelerates oxidative damage, denatures proteins, and raises ionic concentrations to lethal thresholds.
Instrumentation (Parts) of Hot Air Oven
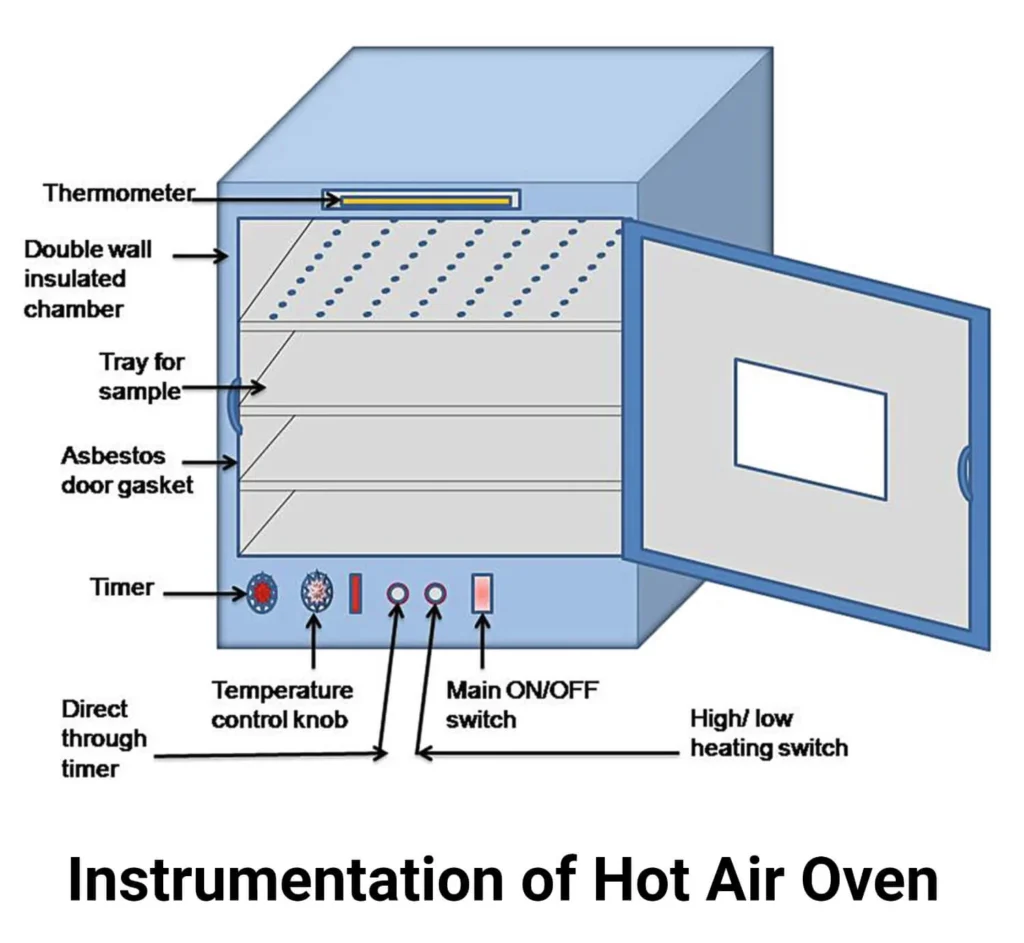
A hot-air oven is primarily reserved for materials that can withstand prolonged heating without melting, deforming, or igniting. At elevated temperatures, the dry heat denatures proteins and subsequently eliminates pathogenic microorganisms and dormant bacterial spores. Reliable sterilization hinges on matching a specific temperature with a corresponding exposure duration that accounts for the target microbe and the physical composition of the load. Standard dry-heat protocols include 170 C for thirty minutes, 160 C for sixty minutes, and 150 C for a full 150 minutes.
Advantages of Hot Air Oven
- A hot-air oven achieves microbial kill without the water or steam of a conventional autoclave.
- Operating costs are modest, and the control interface typically requires little more than a start button.
- Most models reach working temperatures around 180 C, completing cycles in a fraction of the time an autoclave needs.
- Compact benchtop designs occupy a footprint smaller than an office printer and plug into a standard wall socket.
- Because the workflow relies solely on circulating dry heat, metal tools and glass slides emerge rust-free.
- The internal chamber is shallow enough that a researcher can reach in without awkward maneuvers.
- Relative to an autoclave cylinder, the unit builds only a few psi of overpressure, reducing the risk of explosive failure.
- No liquid disinfectants or volatile compounds are employed, so no corrosive residue coats the tray after cooling.
- The even airflow carries heat deep into dense items such as porcelain syringes, ensuring lethal temperatures reach every interior surface.
Bionics HOT AIR OVEN Dimensions
| Model No. | Inner Chamber (W x D x H) |
Volume (Liters) |
Load (KW) |
Shelves (No’s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BST/HAO-1122 | 300 x 300 x 300 mm | 30 | 1.5 | 2 |
| BST/HAO-1123 | 355 x 355 x 355 mm | 45 | 1.5 | 2 |
| BST/HAO-1124 | 455 x 455 x 455 mm | 95 | 2.0 | 2 |
| BST/HAO-1125 | 455 x 455 x 605 mm | 125 | 2.2 | 3 |
| BST/HAO-1126 | 605 x 605 x 605 mm | 224 | 2.5 | 3 |
| BST/HAO-1127 | 605 x 455 x 910 mm | 252 | 2.5 | 3 |
| BST/HAO-1128 | 605 x 605 x 910 mm | 336 | 3.0 | 3 |
Key Points:
- Sterilization Method: Dry heat (not moisture-based like autoclaves).
- Common Temperature: 160°C for 2 hours or 180°C for 30 minutes.
- Applications: Glassware, metal instruments, powders, and oil-based substances.
Applications of Hot Air Ovens
Hot air ovens are used in various fields for different purposes:
- Medical: Sterilizing surgical instruments, glassware, and other medical tools.
- Laboratory: Drying samples, sterilizing equipment, and preparing materials.
- Industrial: Curing paints and coatings, drying materials, and heat treating products.
For example, in a medical setting, a hot air oven might be used to ensure that surgical instruments are free of any viable microorganisms before use in procedures.
Benefits of Using a Hot Air Oven
- Efficiency: Hot air ovens can handle large volumes of items, making them ideal for high-volume settings.
- Safety: Dry heat sterilization is a reliable method that doesn’t involve moisture, reducing the risk of rust and corrosion.
- Versatility: They can be used for a wide range of applications, from sterilizing equipment to curing industrial materials.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Proper maintenance ensures the optimal performance of hot air ovens:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the chamber and racks regularly to prevent contamination.
- Routine Inspections: Check the heating element, fan, and thermostat for any signs of wear or damage.
- Calibration: Ensure the thermostat is accurately calibrated for precise temperature control.
- Troubleshooting: Address common issues such as uneven heating or temperature fluctuations promptly to maintain efficiency.
Conclusion
Air heated ovens are important equipment in various industries, providing a reliable and efficient method for material heating and drying. Their ability to maintain stable temperatures and handle large amounts of material make them indispensable in medical, laboratory and industrial environments. How they work and taking proper care of them is essential in maintaining the highest hygiene and safety standards. In this hot air oven video, we have explained the manufacturing procces of Hot Air Ovens
At Appfinz Technologies, we ensure every technical detail on your product page helps users make informed choices. Whether you’re exploring advanced lab equipment or reliable heating solutions like a hot air oven, our goal is to present clear, SEO-friendly content that aligns with your brand and boosts visibility.

