- What is an Autoclave?
- How to Use an Autoclave Machine
- Autoclave Diagrams
- Best Autoclave Price in India
- The Principle of Autoclave
What is an Autoclave?
At its core an autoclave is a pressurized vessel designed to use moist heat for the physical method of sterilization. often referred to as a steam sterilizer it relies on a specific combination of water pressure and heat to perform its job.
These machines are essential pieces of biotechnology equipment and are used to carry out critical industrial and scientific processes. Whether it is a small unit in a dental office or a large industrial autoclave, the goal remains the same total pathogen destruction.
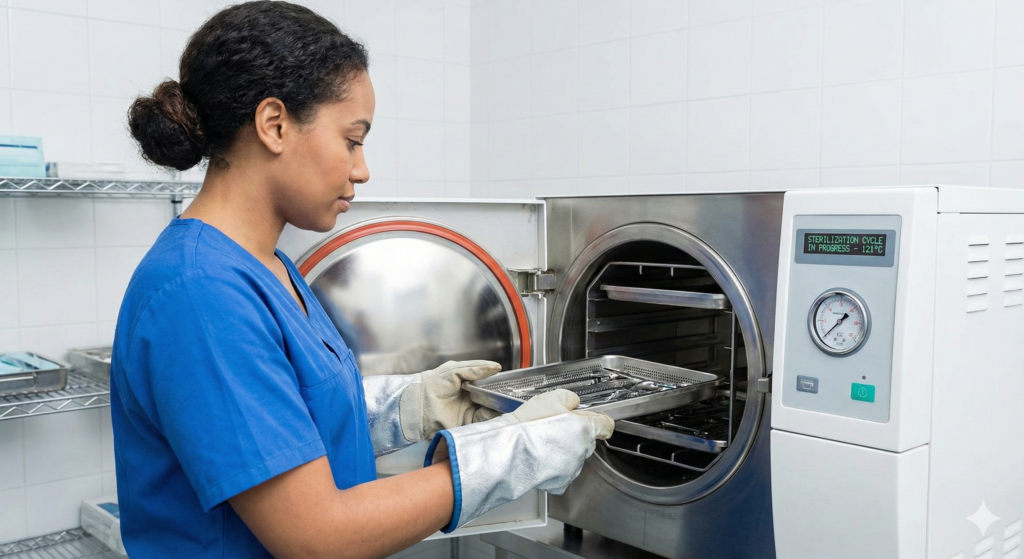

Searching for a reliable laboratory autoclave that is both ISO 9001 and CE certified?
Bionics Scientific Laboratory Autoclaves deliver efficient, safe, and consistent sterilization for all your critical lab and medical procedures. Choose our certified range for guaranteed performance and pressure stability. Contact our experts at info@bionicsscientific.com or call +91 9111161955 | 9376651333.
How Does the Sterilization Process Work?
The secret to why an Autoclave works so well is not just the heat it is the pressure. when steam is placed under high chamber pressure, its temperature can rise far above the normal boiling point of water.
Why 121°C is the Magic Number
Most sterilization protocols require the chamber to reach 121 degrees celsius. at this specific temperature saturated steam effectively kills microorganisms by destroying their proteins through a process called coagulation that ensures thorough microbial decontamination of all items inside.
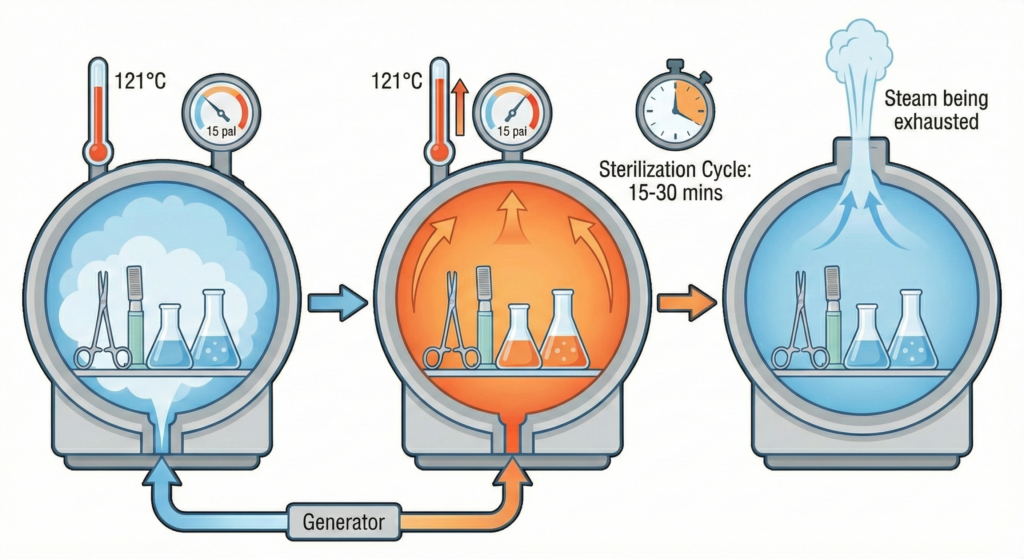
Sterilization cycle phases
A standard sterilization cycle typically consists of three main stages.
- Heating/Purge Phase: Air is removed from the chamber and replaced with steam.
- Sterilization Phase: The temperature and PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) are held constant for a set amount of time (usually 15 – 30 minutes).
- Exhaust/Cooling Phase: The pressure is gradually released and the items are allowed to cool before they are safely removed.
Manual vs. Automatic Autoclaves: A Quick Comparison
Choosing the right type of equipment depends on your specific needs and how often you plan to use it.
| Feature | Manual Autoclave | Automatic Autoclave |
| Operation | Requires manual control of valves and timers. | One-touch operation with digital cycles. |
| Precision | Relies on the operator’s expertise. | High precision with automated sensors. |
| Maintenance | Simpler mechanics, but needs closer monitoring. | Self-diagnostic features for easier care. |
| Ideal Use | Small labs with basic sterilization needs. | Busy hospitals and high-volume labs. |
Key Features and Buying guide
When looking for a Laboratory Autoclave or a medical unit you should focus on features that ensure long term reliability and safety.
- Validation and Calibration: a professional machine should be easy to validate and calibrate to make sure it hits the required temperature and pressure every single time.
- Chamber Durability: look for high grade stainless steel chambers that can handle daily heavy use and high PSI.
- Safety Interlocks: modern units should have doors that cannot be opened until the pressure has Safe to open.
5 Tips for choosing the right unit
- Size: Choose a capacity that fits your largest tools without overcrowding.
- Material: Ensure the interior is corrosion resistant.
- Pressure Range: Verify the machine can handle the specific requirements of your protocols.
- Automation: Decide if you need the speed and ease of an automatic system.
- Service Support: Only buy from providers who offer technical support and spare parts.
3 Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even the best medical sterilization equipment can fail if used incorrectly Avoid these three common errors.
- Overloading: If you pack the chamber too tightly the steam cannot circulate leaving cold spots where bacteria might survive.
- Incorrect settings: Always double check that you have selected the correct time and temperature for the material you are sterilizing
- Skipping maintenance: Regular checks are vital without periodic maintenance seals can leak and sensors can drift.
How to Use an Autoclave Machine
Sterilization is the most critical factor in maintaining safety within medical and research environments. whether you are working in a busy surgical ward or a high tech research facility, knowing how to use autoclave machine equipment properly is a non negotiable skill.
An autoclave machine is a powerful device that utilizes saturated steam and high pressure to kill harmful bacteria viruses fungi and spores that standard disinfectants simply cannot eliminate.
In this guide, we will break down the entire process from understanding the autoclave machine parts to executing a perfect sterilization cycle to ensure your lab remains safe and compliant.
Autoclave Machine How Does it Work?
The machine works on the principle of thermal energy. When water is heated under high chamber pressure it turns into saturated steam. this steam carries significantly more energy than boiling water allowing it to penetrate the cell walls of microorganisms and destroy them instantly.
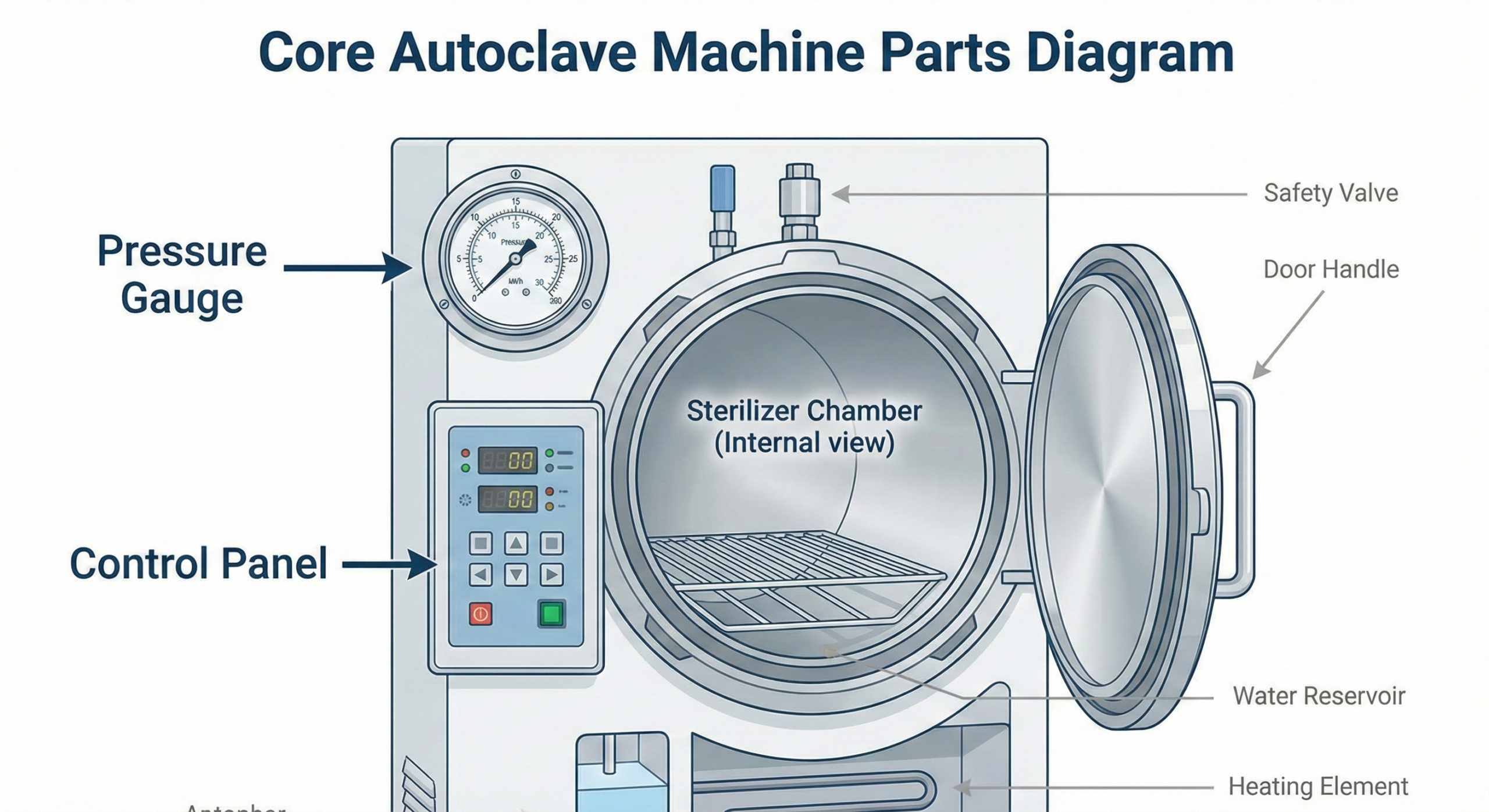
Core Autoclave Machine Parts You Should Know
Before operating the unit it is essential to understand the machine autoclave diagram and its internal components
- Sterilizer chamber – this is the main interior space where you place the items to be sterilized.
- Base chamber – the area where water is stored and heated to produce steam.
- Drain strainer – located at the bottom of the chamber it must be kept clean to allow proper AIR and steam flow.
- Pressure gauge – displays the chamber pressure in Pounds per Square Inch.
- Control panel – usually features a power switch and A green button to start the cycle.
Technical Details: Temperature and PSI
For an autoclave machine to be effective it must reach specific technical benchmarks standard sterilization protocols usually require the autoclave machine temperature to reach 121°C (250°F).to achieve this temperature the machine must increase the internal chamber pressure to 15 PSI. this combination of heat and pressure ensures that even the most resilient biological threats, such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus (the biological indicator used for testing) are completely destroyed.
Autoclave Cycle Reference Table
| Parameter | Recommended Setting | Purpose |
| Autoclave Machine Temperature | 121°C | Kills spores and viruses |
| Chamber Pressure | 15 PSI | Reaches necessary heat levels |
| Cycle Time | 15–30 Minutes | Ensures full penetration |
| Biological Indicator | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | Validates sterilization success |
Pre-Operation Checklist
A successful sterilization cycle starts before you even turn on the autoclave machine. follow these safety and maintenance steps.
- Check the drain : Ensure the drain strainer in the bottom of the autoclaves sterilizer chamber is clean If it is clogged the steam wonot circulate, and your items wonot be sterile.
- Water level : Check the base chamber You usually need to fill approximately one liter of water in the base chamber use distilled water to avoid mineral buildup).
- Inspect your load : Ensure all items are autoclave safe Never put volatile chemicals or heat sensitive plastics inside.
- Prepare safety gear : Always have heat resistant gloves nearby Steam burns are a serious risk when operating an autoclave machine for hospital or lab use.
Step by Step teach to Using an Autoclave Machine
Now that you are prepared follow these steps to use autoclave machine systems effectively.
Step 1 – awareness
Ensure the power is connected Open the chamber door and verify that the drain is clear of debris Add the required one liter of water to the base.
Step 2 – Loading the Items
Place your instruments or glassware into the sterilizer chamber. Do not crowd the items; steam must be able to touch every surface of every object.
- Expert Tip – Use autoclave tape .indicator strips on the outside of your packages. These strips change color once the correct cycle time and temperature are reached, giving you visual proof of sterilization.
Step 3 – Sealing and Starting
Close the door and lock it securely Check the settings on the control panel Once ready press the Green button on the right front of the machine This will begin the heating process and start building the necessary chamber pressure.
Step 4 – Sterilization phase
the machine will now use pressurisation steam to kill any microbial life Monitor the autoclave machine temperature to ensure it hits 121°C. The PSI should stabilize around 15 The cycle will typically run for 20 minutes once the target temperature is reached.
Step 5 – Exhaust and cooling
after the cycle finishes the machine will release the pressure Wait until the pressure gauge reads zero before attempting to open the door.
Step 6 – Unloading
Carefully open the door just a crack to allow the remaining steam to escape After a few minutes use your heat resistant gloves to remove the items Let them air dry completely before storage.
Why use an autoclave machine for hospital and lab safety?
the primary reason we rely on the autoclave machine is its capability to handle biohazardous waste and reusable medical tools Standard washing or even chemical baths can leave behind spores Because a autoclave machine uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores it provides the highest level of decontamination possible.
In a hospital setting the autoclave machine for hospital use is the gold standard. It ensures that surgical tools are 100% sterile, reducing the risk of post operative infections and saving lives.

Maintenance and Best Practices
To keep your autoclave machine running at peak performance follow these maintenance tips
- Daily Cleaning – always check the drain strainer A small piece of paper or debris can cause a cycle to fail.
- Weekly Testing – use a biological indicator like Geobacillus stearothermophilus once a week. If the bacteria survive the cycle your autoclave machine needs immediate repair.
- Monitor the Seals – the door gasket is vital for maintaining chamber pressure If you notice steam leaking from the door the gasket needs to be replaced.
- Professional Calibration – have a technician check the autoclave machine temperature and pressure gauges annually to ensure they are accurate.
Conclusion
Understanding how to use autoclave machine equipment is essential for anyone in the medical or scientific field By paying attention to the autoclave machine parts maintaining the correct PSI, and following a strict step by step process, you can ensure that every item you process is safe for use.
Whether you are sterilizing glass for a research project or preparing tools in a hospital the autoclave machine remains your most reliable partner in the fight against infection For more technical details on high-quality sterilization equipment, you can visit professional resources like Bionics Scientific to see the latest in laboratory technology.
Autoclave Diagrams
Sterilization is the backbone of any scientific or medical environment yet the machinery involved can often feel like a black box of complex pipes and valves. If you have ever stared at a complex autoclave diagram and felt overpower you are not alone. Understanding how these machines work is not just for technicians it is essential for microbiology students, lab experts, and medical professionals who rely on sterile ecological disasters every day.
An autoclave is essentially a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes that require elevated temperature and pressure. It is the gold standard for moist heat sterilization,ensuring that even the most stubborn bacteria are wiped out. In this guide, we will break down the autoclave machine diagram into simple, understandable parts so you can master its functions.
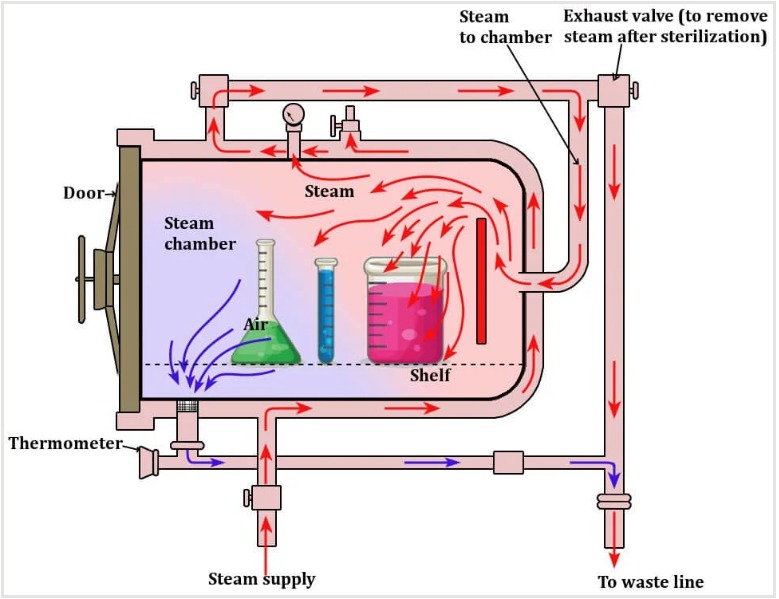
Anatomy of an Autoclave Key Components
To truly understand a schematic diagram of autoclaves you need to know the role each part plays. A high quality autoclave diagram with label typically highlights several critical components that work in harmony to create a pressurized high heat environment.
1. The Pressure Vessel and Outer Jacket
The heart of any autoclave diagram is the pressure vessel. This is the inner chamber where you place your laboratory media or surgical tools. Most modern units also feature a jacketed chamber an outer layer that surrounds the inner vessel to help maintain consistent temperatures and reduce condensation.
2. Steam Generator (The Boiler)
Often referred to as the powerhouse of the unit the steam generator heats water to produce saturated steam This steam is what actually performs the sterilization.
3. Safety Valve and Pressure Gauge
Safety is paramount when dealing withs high pressure steam Every autoclave diagram simple enough for an beginner will always feature an safety valve. This component acts as a fail safe releasing excess pressure if it exceeds the chambers limits. The pressure gauge allows the operator to monitor the internal environment in real time.
4. Gasket Seal
the gasket seal is a heavy duty rubber or silicone ring that ensures the door remains airtight. Even a tiny leak in the gasket can prevent the machine from reaching the necessary pressure rendering the sterilization cycle ineffective.
5. Thermostatic Trap
This is a specialized valve thats allows air And cooled water (condensate) to exit the chamber while trapping the HOT steam inside. Efficient air displacement is key to preventing cold spots inside the machine.
Horizontal vs Vertical Autoclave: Which Diagram Fits Your Lab?
When choose a sterilizer you will likely encounter two main structural designs. Both follow similar scientific principles but differ in how they are loaded and where they fit in your Workspace.
Comparison Table: Vertical vs. Horizontal Structures
| Feature | Vertical Autoclave | Horizontal Autoclave |
| Loading Style | Top-loading (items stacked) | Front-loading (items on shelves) |
| Space Efficiency | Compact; ideal for small labs | Requires more floor space |
| Capacity | Limited by vertical stacking | High capacity for bulky loads |
| Best Used For | Microbiology media, small flasks | Hospitals, large-scale industrial use |
| Structure | See vertical autoclave diagram | See horizontal autoclave diagram |
The Role of an Autoclave Diagram in Microbiology
In a biological setting the autoclave diagram in microbiology is slightly more specialized. It often emphasizes the sterilization of biohazardous waste and laboratory media Microbiologists use the machine to hit the thermal death time” of resilient organisms like Geobacillus stearothermophilus (the standard biological indicator).
Using a simple autoclave diagram as a reference students can learn how to avoid common pitfalls such as trapping air in bottles or failing to reach the holding time” required for total decontamination.
Standard Sterilization Parameters
Every autoclave machine diagram is designed to help the unit reach these specific industrial standards.
- Temperature : 121 degrees Celsius.
- Pressure : 15 PSI.
- Cycle Type : gravity displacement or vacuum pulse.
when the machine hits 121 degree at 15 PSI it creates an environment where moist heat can penetrate porous materials and kill microbial life at a cellular level.
5 Things to Consider Before Buying an Autoclave
Selecting the right unit involves more than just looking at an autoclave diagram simple layout. Consider these professional factors
- Chamber Volume : Ensure the internal pressure vessel is large enough for your most common load sizes.
- Cycle Speed : Some horizontal autoclave models offer rapid cooling phases to save time.
- Ease of Maintenance : look for designs where the gasket seal and thermostatic trap are easy to clean or replace.
- Material Quality : high grade 304 or 316 stainless steel is essential for longevity.
- Digital Controls : modern units offer automated sterilization cycles reducing the risk of human error.
Common Mistakes and Maintenance Tips
Even with a perfect autoclave diagram with label to guide you mistakes can happen Watch out for these common issues
- Gasket Leaks: Regularly check the door seal for cracks A faulty gasket is the the first cause of pressure loss.
- Incorrect Loading: Never overcrowd the chamber Steam must be able to circulate freely around every item.
- Ignoring the Pressure gauge : Always verify that the gauge matches the digital readout to ensure accuracy.
- Clogged Drains: Ensure the thermostatic trap is clear of debris to allow proper air displacement.
Wrapping Up
Mastering the autoclave diagram is the first step toward becoming a pro in the lab Whether you are studying a vertical autoclave diagram for your university finals or managing a horizontal autoclave diagram in a busy hospital knowing your components from the safety valve to the steam generator is vital for safety and success.
Best Autoclave Price in India
Choosing the right sterilization equipment is a critical decision for an medical laboratory or professional facility. Whether you are setting up a new dental clinic or upgrading a hospital wing understanding the autoclave price and the technical features that drive it is essential. Reliability in sterilization is not just a regulatory requirement it is A commitment to safety.
Autoclave Price in India: Type & Pricing Breakdown
The autoclave price in India varies significantly based on the technology, capacity, the specific industry it serves From a portable autoclave machine used in small clinics to a high end hospital grade sterilizer each type carries a different price point. Below is a detailed breakdown of the typical price ranges you can expect in the market today.
India Autoclave & Sterilizer Price List (2026)
| Machine Type & Specification | Ideal Application (Best Use) | Estimated Price Range (INR) |
| 1. Portable Autoclave(10L – 25L, Single Wall) | Small Clinics, General Practice, Tattoo Studios | ₹5,500 – ₹12,500 |
| 2. Small / Tabletop Autoclave(15L – 25L, Non-Vacuum) | Dispensaries, Small Labs, OPD Centers | ₹15,000 – ₹45,000 |
| 3. Vertical Autoclave(22L – 100L, Double/Triple Wall) | Microbiology Labs, Pathology, Bio-Waste | ₹25,000 – ₹1,30,000 |
| 4. Horizontal Cylindrical(75L – 300L, High Volume) | Nursing Homes, Small Hospitals (Bulk Loads) | ₹1.50 Lakh – ₹4.80 Lakh |
| 5. Horizontal Rectangular(200L – 500L+, Sliding Door) | Corporate Hospitals, CSSD, Pharma Production | ₹5.50 Lakh – ₹15.00 Lakh |
| 6. Double Door Autoclave(Pass-Through System) | Pharma Cleanrooms, Sterile Barrier Zones | ₹2.90 Lakh – ₹12.00 Lakh |
| 7. Class B Dental Autoclave(18L – 23L, Vacuum Type) | Dental Clinics (Drills), Eye Surgery, Hair Transplant | ₹70,000 – ₹3.40 Lakh |
| 8. Pulse Vacuum Sterilizer(Industrial Grade) | Pharma Manufacturing, Textiles (Porous Loads) | ₹4.75 Lakh – ₹30.00 Lakh |
| 9. Plasma Sterilizer (H2O2)(Low Temp 55°C) | Robotic Surgery, Laparoscopy, Delicate Electronics | ₹11.00 Lakh – ₹72.00 Lakh |
| 10. Dry Heat Sterilizer(Depyrogenation Oven) | Glassware, Ointments, Powder (Endotoxin Removal) | ₹16,500 – ₹20.00 Lakh |
| 11. Rotary Retort Sterilizer(Industrial Food) | Ready-to-Eat Curries, Retort Pouches, Milk | ₹12.35 Lakh – ₹45.00 Lakh |
| 12. Superheated Water Spray(Terminal Sterilizer) | IV Fluids, Sealed Liquid Bottles (BFS) | ₹8.50 Lakh – ₹65.00 Lakh |
| 13. Air Steam Mixture(Ventilator Autoclave) | Pre-filled Syringes, Soft Bags, Blister Packs | ₹10.00 Lakh – ₹50.00 Lakh |
| 14. Cement / Tile Autoclave(High Pressure 300 psi) | Construction Material Testing (Soundness Test) | ₹38,000 – ₹2.05 Lakh |
| 15. Glass Bead Sterilizer(Instant Heat) | Chairside Dentistry (Tips, Files, Forceps) | ₹930 – ₹2,500 |
Factors influencing the Autoclave Machine Price
When researching the autoclave machine price it is important to look beyond just the sticker value. Several technical specification and components play a major role in determining the final steam sterilizer cost..
1. Classification (Class N vs Class B vs Class S)
- Class N : Suitable for simple un wrapped solid instruments. This is usually the most budget friendly autoclave price option.
- Class B : These units feature vacuum cycle sterilization which is necessary for porous or hollow instruments. The b class autoclave price is higher due to this advanced technology.
- Class S : Custom designed for specific types of loads as defined by the manufacturer.
2. Capacity and Components
The size of the chamber such as a small 12L dental sterilizer versus a larger 22-liter autoclave, directly impacts the autoclave price in India Additionally, the quality of components like stainless steel autoclave drum sizes, replacement heating elements, and the durability of the autoclave gasket price will affect long term maintenance costs.
Manual vs. Fully Automatic Autoclave: A Comparison
Choosing between a manual and a fully automatic autoclave depends on your workload and precision requirements.
| Feature | Manual Autoclave | Fully Automatic Autoclave |
| Ease of Use | Requires constant monitoring. | One-touch operation. |
| Precision | High risk of human error. | Digital control of pressure and time. |
| Price | Lower initial autoclave price. | Higher initial autoclave machine price. |
| Drying Cycle | Usually manual. | Includes automatic vacuum drying. |
The utmost show : 5 Things to Check
To ensure you get the best value for your autoclave price follow this checklist before making a purchase
- Material Quality : look for high grade stainless steel (SS 304 or SS 316) for both the chamber and the autoclave drum price considerations to, ensure longevity.
- Certification : Ensure the equipment is certified by relevant bodies (ISO, CE) for safety and performance.
- Warranty & AMC : check if the supplier offers an Annual Maintenance Contract . Low AMC costs can save you significant money over the years.
- GST Impact : Verify the GST on medical equipment in India (typically 12% or 18%) to understand the final landed autoclave price in India.
- Brand Reputation : Compare imported vs. domestic autoclave brands. Domestic brands often offer better budget friendly sterilization equipment with easier access to spare parts.
3 Common Mistakes When Comparing Autoclave Prices
Many buyers make the mistake of choosing the lowest dental autoclave price without considering the operational risks.
- Ignoring the Vacuum Cycle : Buying a Class N machine when you need a b class autoclave price model for hollow tools can lead to sterilization failure.
- Neglecting Maintenance : Using poor quality sterilization indicator tape or ignoring a worn-out gasket can compromise safety.
- Overlooking the Drum : Not checking the autoclave drum price or size can lead to inefficient loading and higher electricity bills.
The Principle of Autoclave
In the world of medical research and healthcare sterilization is not just a preference it is a life saving necessity Whether you are a microbiology student or a lab manager understanding the autoclave principle is fundamental to maintaining a sterile environment. The, autoclave is widely considered the most reliable method for achieving total sterilization in laboratories and hospitals.
What is the focus Principle of Autoclave?
The primary autoclave principle is based on Moist Heat Sterilization Unlike dry heat which takes much longer to kill microbes moist heat uses saturated steam under high pressure to eliminate even the most resilient microorganisms.
The working principle of autoclave relies on the relationship between pressure and temperature. In a normal environment water boils at 100°C which is often not enough to kill bacterial spores However the autoclave principle and working mechanism allow us to increase the internal pressure of the chamber typically to 15 psi This increased pressure raises the boiling point of water, allowing the steam to reach a critical temperature of 121°C.
The Role of Saturated Steam
When we discuss the autoclave principle, the quality of steam matters. Saturated steam is highly efficient because it carries a massive amount of energy known as the Latent heat of vaporization. When this steam contacts cooler surfaces of lab equipment, it condenses and releases this energy, instantly heating the material and killing pathogens. This efficiency is why the working principle of autoclave is superior to other methods.
The Biochemistry: How High Pressure Kills Microbes
To truly grasp the principle of autoclave microbiology we must look at what happens at a molecular level within a microorganism The autoclave principle works through two primary biochemical processes
- Thermal Coagulation of Proteins : High temperature steam causes the proteins and enzymes essential for microbial life to uncoil and clump together Once these proteins are coagulated, the microbe can no longer function.
- Hydrolysis of Macromolecules : The moisture in the steam aids in the Hydrolysis of macromolecules breaking down the cellular structure of bacteria and viruses.
By combining these two processes the autoclave principle and working cycle ensures that no living organism, including highly resistant spores, survives the process.
Step by Step The Working Principle of Autoclave in Action
The actual working principle of autoclave follows a specific cycle to ensure total safety.
1. Air Removal Phase
Before the sterilization begins all air must be removed from the chamber using a vacuum pump or displacement This is a crucial part of the autoclave principle because trapped air acts as an insulator, creating cold spots” where bacteria might survive.
2. Sterilization (Holding Time)
Once the air is gone and the chamber reaches 121°C at 15 psi, the Holding time begins. Under the principle of autoclave microbiology this typically lasts for 15 to 20 minutes to ensure complete penetration of heat.
3. Exhaust and Cooling
After the Holding time the pressure is slowly released through an exhaust valve. If you are preparing an autoclave principle ppt it is important to note that rapid pressure drops can cause liquids to boil over.
Validation: Is the Autoclave Principle Working?
How do we know if our sterilization was successful Validation is a key aspect of the autoclave principle and working protocol.
| Indicator Type | Description | Purpose |
| Chemical Indicators | Autoclave tape that changes color. | Shows the item reached a certain temperature. |
| Biological Indicators | Uses Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores. | The ultimate test if these spores die, the cycle was successful. |
Safety First
While the autoclave principle is highly effective it involves high pressure and heat Always check the Safety Valve and Pressure Gauge before use and never forget your heat resistant gloves.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure the working principle of autoclave remains effective avoid these common errors
- Overloading : Packing items too tightly prevents saturated steam from reaching all surfaces.
- Improper Air Displacement : Ensure the vacuum pump is working to avoid cold spots”.
- Ignoring the Rule : The core autoclave principle relies on the 121°C / 15 psi / 15 min rule. Shortcutting any of these factors compromises safety.
Conclusion
Mastering the autoclave principle is essential for any laboratory professional By utilizing Moist Heat Sterilization the thermal coagulation of proteins and the power of latent heat we can achieve a level of cleanliness that keeps our science and our patients safe.
Whether you are studying the principle of autoclave microbiology or preparing an autoclave principle ppt for your team always prioritize the fundamental physics of pressure and temperature.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the working principle of an autoclave?
The focus autoclave principle is based on moist heat sterilization. It uses saturated steam under high pressure to kill microorganisms by causing the thermal coagulation of proteins and the hydrolysis of macromolecules.
2. Why is 121 degrees Celsius the standard temperature for sterilization?
At 121°C (250°F) saturated steam carries enough energy to destroy even the most resilient biological threats such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus Spores This temperature is achieved by increasing the internal chamber pressure to 15 PSI.
3. How long does a standard autoclave cycle take?
While the entire process includes heating and cooling the sterilization phase (holding time) typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes once the target temperature and pressure are reached.
4. What are the three main stages of an autoclave cycle?
A standard cycle consists of
- Heating/Purge Phase : Air is a removed and replaced with steam.
- Sterilization Phase : Temperature and pressure are held constant for the set time.
- Exhaust/Cooling Phase : Pressure is gradually released so items can cool.
5. What is the difference between a manual and an automatic autoclave?
Manual units require the operator to control valves and timers and are generally cheaper Automatic autoclaves offer one touch operation higher precision with sensors, and automated drying cycles making them ideal for busy hospitals.
6. What are the most important parts of an autoclave machine?
Key components include the pressure vessel (the chamber) the steam generator (boiler) the safety valve (to release excess pressure) the pressure gauge and i the gasket seal which ensures the door is airtight.
7. Should I choose a vertical or horizontal autoclave?
It depends on your space and needs Vertical autoclaves are top-loading and compact great for small labs. Horizontal autoclaves are front loading, offer higher capacity for bulky loads and are commonly used in large hospitals.
8. What is the price of an autoclave machine in India?
The autoclave price in India varies by type:
- Portable – 5,000 to 18,000. rs
- Vertical – 25,000 to 1,80,000. rs
- Horizontal – 1,50,000 to 6,00,000. rs
9. What is a Class B autoclave?
A Class B autoclave uses vacuum cycle sterilization which is necessary for sterilizing porous or hollow instruments Because of this advanced technology the price is generally higher than Class N units.
10. How do I know if my autoclave is working correctly?
Validation is done using chemical indicators (like autoclave tape that changes color) and biological indicators The ultimate test is using Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores if they are killed during the cycle sterilization was successful.
11. Why is air removal important in an autoclave?
Trapped air acts as an insulator creating cold spots” where steam cannot reach This prevents the items from reaching the necessary temperature, potentially allowing bacteria to survive.
12. What common mistakes should I avoid when using an autoclave ?
Overloading Steam must be able to circulate around every item.
- Incorrect Settings : Using the wrong time or temperature for the specific material.
- Ignoring Maintenance : Failing to check the gasket or clean the drain strainer.
13. What maintenance is required for an autoclave?
Daily maintenance includes cleaning the drain strainer Weekly, you should perform biological testing. Annually a professional technician should perform calibration of the temperature and pressure gauges.
14. What safety precautions should be taken ?
Always wear heat resistant gloves to prevent steam burns Never attempt to open the door until the pressure gauge reads zero and ensure the safety valve is functional to prevent over pressurization.
15. Can I sterilize any material in an autoclave?
No. Only autoclave safe” items should be processed. You must never put volatile chemicals or heat-sensitive plastics inside as they can explode or melt.



