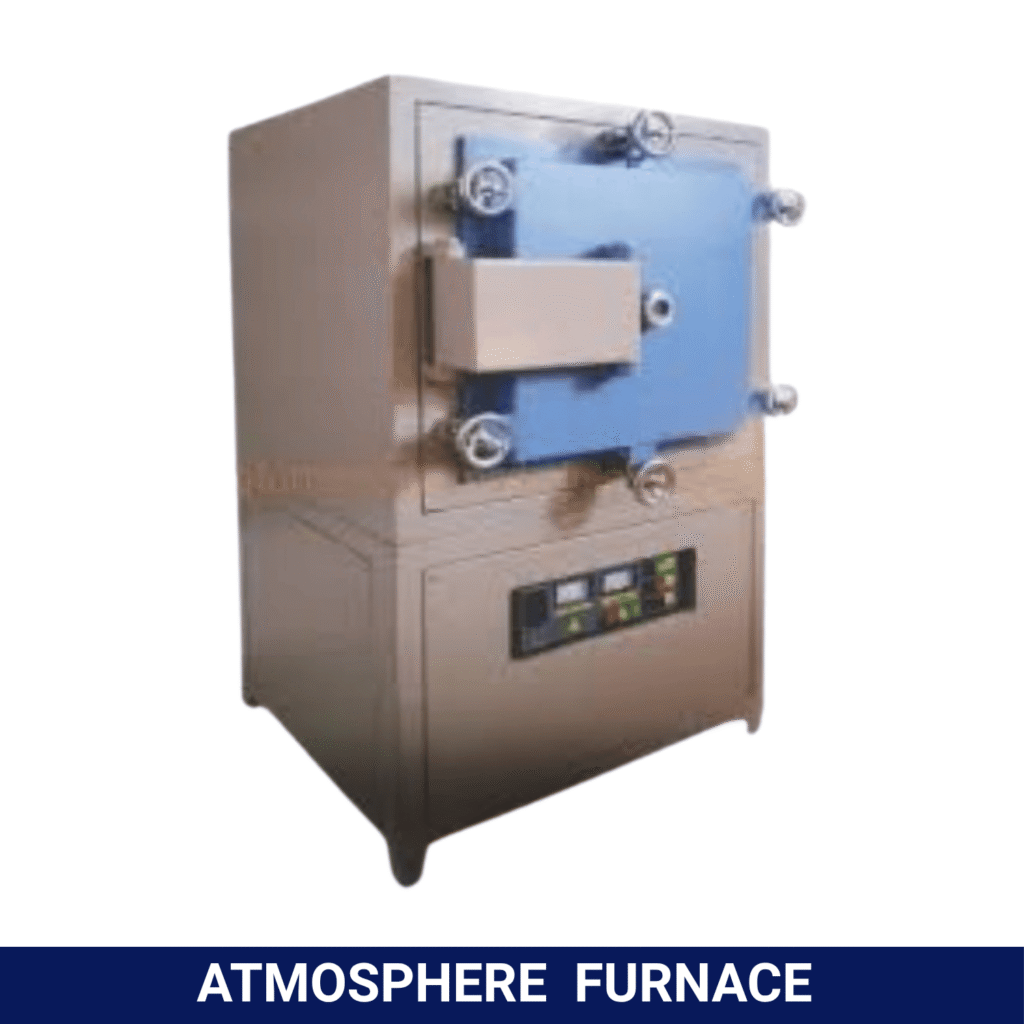
Laboratory furnaces are very effective tools in scientific and industrial research, These are known for their ability to deliver precise high-temperature conditions. From ashing and heat treatment to material testing and sintering, these laboratory furnaces play a crucial role in ensuring accurate results and supporting a wide range of experiments and processes. In this blog, we’ll explore the five best uses of laboratory furnaces and how they contribute to efficient lab operations.
Usage of furnace in laboratory
Laboratory furnaces provide a chamber where scientists keep samples at precisely controlled high temperatures. These temperatures can range from a few hundred degrees to thousands, such as melting metals or hardening ceramics.
Use of furnace in laboratory
- Material processing: Furnaces help to change raw materials. They are used to dry out samples, removing moisture and preparing them for further analysis. Heat triggers chemical reactions within materials while hardening resins or paints. Furnaces also help in sterilization which kills microorganisms with the help of high temperatures.
- Thermal analysis: Scientists use furnaces to study the effects of heat on materials. They look for changes in the material’s weight, size, or physical properties, such as conductivity. Techniques such as annealing use controlled heating and cooling to improve metals’ malleability and strength.
- Chemical analysis: Furnaces are also used in many chemical processes. Ashing burns samples to reveal their inorganic content. Elemental analysis heats samples to high temperatures to identify their constituent elements.
- Materials development: Furnaces are used in research and development labs to create new materials or improve old ones. Sintering uses powdered materials together to change strong components without melting them. Furnaces are also used to create new alloys and study their properties at high temperatures.
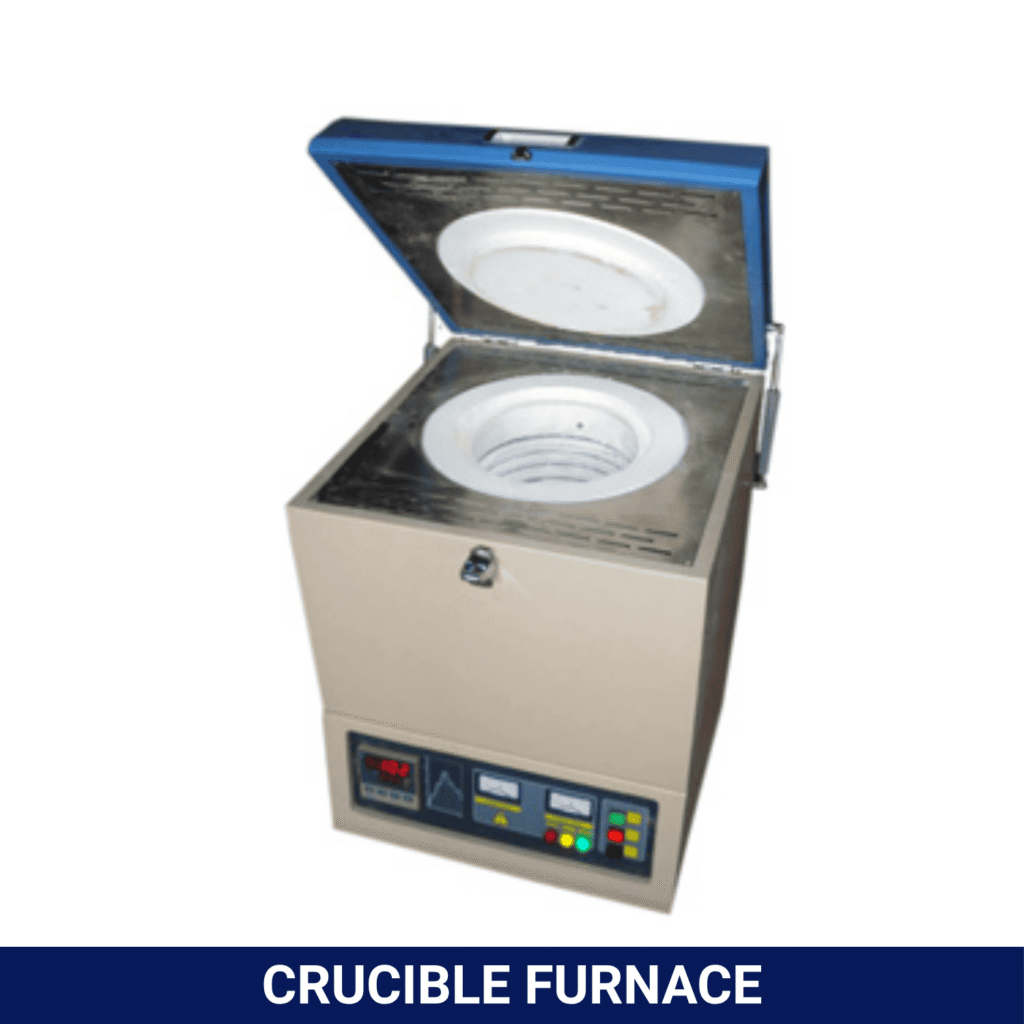
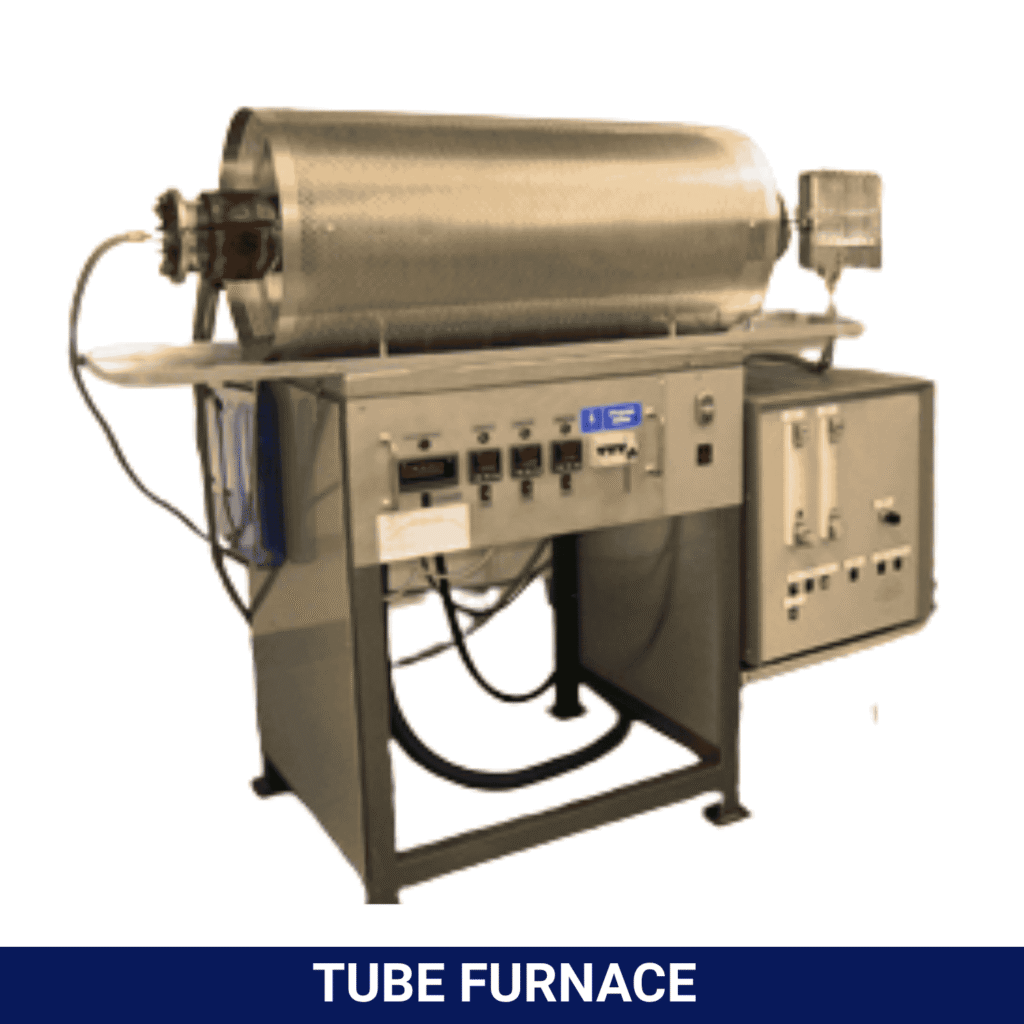
There are several types of lab furnaces designed for different purposes. Box furnaces are for general applications. Tube furnaces provide heated tubes for continuously processing samples. Crucible furnaces are designed to melt metals at very high temperatures.
Furnaces also help with lab safety: Furnace has many features. It can control temperature, It can alarm, and heat shields that reduce the risk of burn or overheating.
🔬 5 Best Things About the Use of Furnace in Laboratory
- High-Temperature Precision
Furnaces offer accurate and consistent heating up to 1800°C, ideal for ash content determination, sintering, and sample combustion. - Versatile Applications
Used across chemistry, metallurgy, ceramics, and environmental testing, lab furnaces support a broad range of scientific tasks. - Contamination-Free Environment
Muffle furnaces ensure clean combustion by isolating the sample from direct flame or combustion gases, improving test reliability. - Programmable Control Systems
Modern lab furnaces feature digital PID controllers, allowing precise programming of temperature ramps and hold times. - Efficient & Safe Operation
Designed with advanced insulation, safety interlocks, and over-temperature protection, they deliver secure and energy-efficient performance.
Looking for Laboratory Furnaces ?
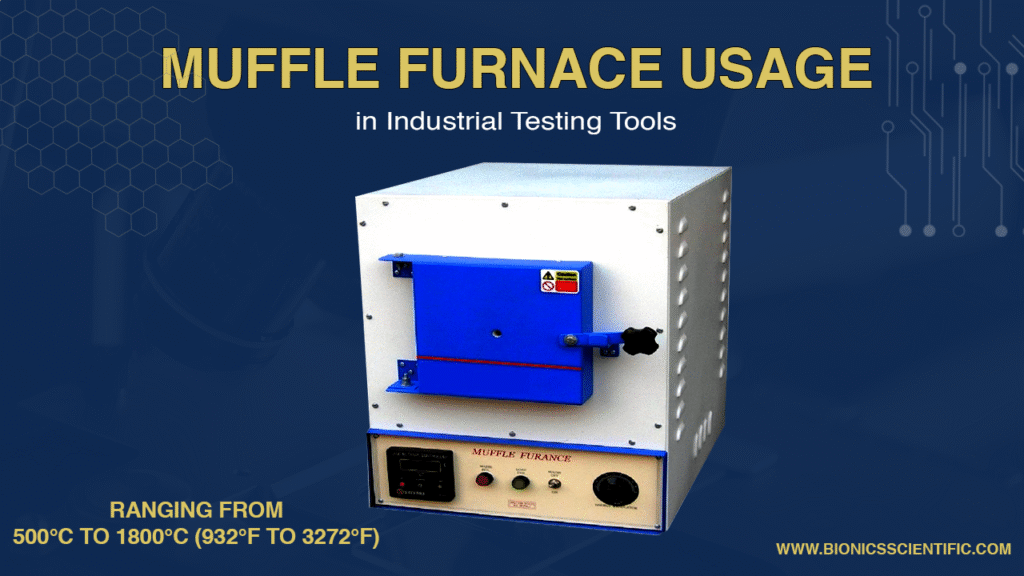
Bionics Scientific is a Delhi based India’s leading manufacturer of muffle furnaces for laboratory manufacture muffle furnace ranging from 500°C to 1800°C (932°F to 3272°F). Call Us +91 9111161955, 9376651333 | Email us: info@bionicsscientific.com
Usage of Furnace in Laboratory
Laboratory furnaces, especially muffle furnaces, are essential for high-temperature applications that require precise heat control and a contamination-free environment. These furnaces are widely used in research labs, quality control departments, educational institutions, and various industrial sectors.
Common Uses of Laboratory Furnace Includes:
- Ash Content Analysis: Determining the inorganic residue in materials like food, coal, plastic, and pharmaceuticals after combustion.
- Heat Treatment of Metals: Processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering of metallic samples under controlled temperatures.
- Material Testing: Evaluating how materials behave under extreme heat — important for quality assurance and R&D.
- Sintering and Firing: Used in ceramics and glass industries for bonding materials and achieving final hardness and strength.
- Gravimetric Analysis: Removing volatile substances from a sample to measure weight changes during combustion.
- Organic Matter Removal: In environmental and soil labs, furnaces burn off organic components to prepare samples for analysis.
When you witness a scientific breakthrough, remember the silent contribution of this laboratory furnace. Whether creating life-saving medical implants or developing the materials of the future, this instrument plays a vital role in scientific discovery.